Payment gateway:
A payment gateway is a platform or a service that helps authenticate cardholders’ details for offline and online businesses.
It, being equivalent to a POS machine, requires the customer of a merchant to fill in the card details in the slots created for the same.
Post submission of the details, a payment gateway makes for the secure channel that flows the information from the customer to the merchant and then between the merchant and the bank ahead.
Types of Payment gateway:
- Hosted payment gateways-
Such gateways, during the checkout, take the customer away from the site’s checkout page and redirect to the Payment Service Provider page (PSP).
Hence, when the customer clicks on the gateway link and is redirected, he/she needs to fill in the payment details.
Post this, the page is redirected back to the merchant’s website to finish the checkout/payment process.
- Self-hosted payment gateways-
Self-hosted gateways are the channels, which allow the payment details to be taken from the customers within the merchant’s website alone.
Following this, the data is sent further to the payment gateway’s URL. While some gateways need the payment details to be provided in a specific format, there are others, which require merely a hash key or a secret key.
- API hosted payment gateways-
The API-hosted gateways allow the customers to enter their credit or debit card details directly on the merchant’s checkout page.
Following this, the payments are processed using an API (Application Programming Interface) or HTTPS queries.
- Local bank integration-
These gateways, upon checkout, take the customer to the payment gateway’s website (bank’s website). On this site, the customer is required to enter the payment details and the contact details.
This allows the payment to happen and the customer gets redirected again to the merchant website. Also, the payment notification and the data get sent upon redirection.
Nodal Account:
A nodal account is an account, which enables the merchants to process online credit and debit payments successfully.
A payment gateway helps to deposit the funds from the customer’s credit card for sales in the nodal account.
Thereafter, the amount gets automatically and directly transferred into the merchant’s business bank account from the merchant’s account.
Why cannot the amount work its way directly into the business bank account?
Now as the amount goes first in the nodal account and then the acquirer’s bank account, it is but obvious that a merchant would prefer that the amount be directly transferred into the business bank account. The reason this is not the route has two valid points:
Number one, since at any point in time merchandise may be returned, there is a chance that some amount you receive as an e-commerce platform will be paid back.
This happens by subtracting what is kept in the merchant’s account immediately. If not done so, it may account for some level of risk in the transactions.
The amount returned, then, is removed from the total amount, and the rest is transferred to the business bank account.
Number two, the payment gateway keeps accumulating deposits from multiple sources/customers. If, while doing so, it keeps transferring each deposit individually it will have to transfer five separate deposits.
On the contrary, the payment gateway gathers all the deposits in the nodal account and directly transfers the entire amount as one single deposit.
This process makes reconciliation much simpler and easier to handle.
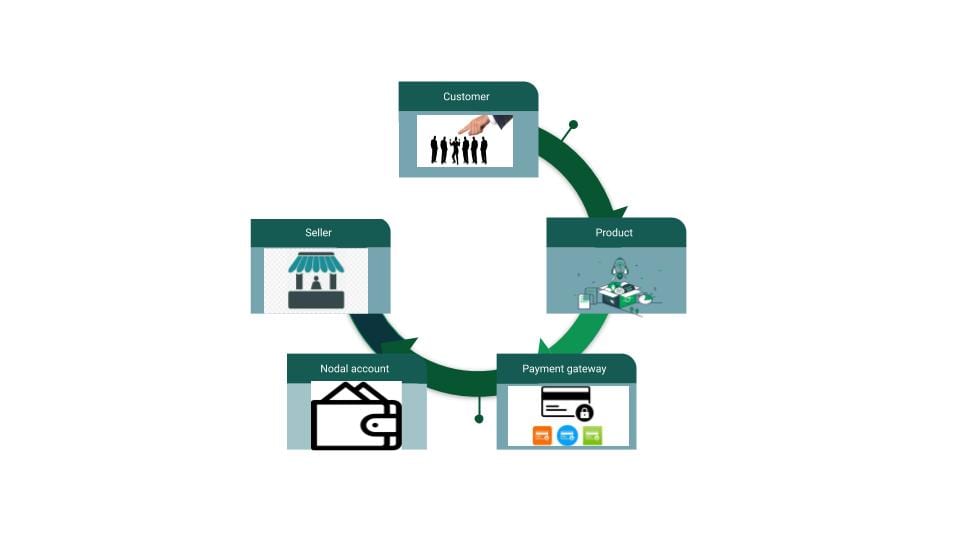
The image above shows the flow of payment starting from the purchase by the customer to the settlement of the amount in the Seller’s bank account.
Step 1: The customer makes the purchase of a product from an e-commerce website.
Step 2: Amount is furthered via Payment Gateway integrated with the website to the Nodal account where it stays till the status shows “customer satisfaction” with the product.
Step 3: Payment proceeds from the Nodal account to the Seller’s bank account if customer satisfaction is achieved.
Harmony between a Payment gateway and a Nodal account
For any e-commerce platform, it is vital to understand and pick that payment gateway, which can enable transactions to flow in smoothly, safely, quickly, and conveniently.
Adding on to it, a payment gateway’s functional qualities are incomplete without an additional facility, which is a Nodal account.
Going hand-in-hand, both the services together allow a merchant to make the everyday transactions simpler, more organized, and possible from even different parts of the world.
Conclusively, the only major difference between a payment gateway and the nodal account is that one is the channel to flow the transaction from the cardholder’s account while the other is the platform where it sits for a while until it is further flown to the merchant’s business bank account.